e-Pramaan: A National Authentication Service along with Aadhaar
Need for e-Pramaan:
In the current digital world more and more applications/services are offered online at citizen’s doorstep. The spread of web and mobile services has surely simplified life of citizens; however, it has also made it vulnerable. A wall of security which was there due to one’s physical presence is now removed. Possibility of stealing one’s valuable data by forgery is a threat if proper security measures are not taken.
Some of the online services are trying to secure the data and communication by authenticating the user through login- password mechanism. The approach, however, has multiple limitations such as:
- Not Standard Based - The implementations may not be standard-based and may have security loopholes.
- Single way Authentication - The authentication mechanism provides only one-way authentication. Only service user gets authenticated to the service, however, the authenticity of the service may not be guaranteed to the User. User may be accessing a phishing site and is unaware of it.
- Multiple Logins – Users have to remember many logins and passwords to access various services which become a tedious task and users start maintaining login-password list which defeats the whole purpose.
- Authentication Mechanism Change – Sometimes online services realize that the data they are sharing is more sensitive and will need stronger authentication to improve security. If authentication is implemented at every service level, there are time, cost and effort implications.
A centralized authentication mechanism like e-Pramaan may help solve these issues.
NCMC Ecosystem Development
When we identify a person, we use certain attributes such as looks, voice etc. For a computer to recognize a person, below factors can be used.
- Something User knows (e.g. a password, answer to the security question): This is the most common kind of authentication used in online services. We use passwords every day to access our systems. Unfortunately, it is very vulnerable as a user may forget or share or misplace which someone else can guess or get to use.
- Something User Has (e.g. a smart card, Digital certificate, Software Token, GRID): This form of human authentication removes the problem of forgetting something you know, but it should be in possession while using it for authentication. And such an object might be stolen.
- Something User Is (e.g. biometric such as fingerprint, IRIS, Voice, Face): It's much harder to lose a fingerprint than a wallet. For this kind of authentication special devices like a fingerprint scanner, IV cameras may be required.
As seen above, each of the authentication methods has its merits and demerits. None of the above methods may be singled out as foolproof identification and authentication of an individual. The most useful form of authentication will be a combination of these which are commonly known as multifactor authentication.
Envisaging these issues with the growth of Digital India, Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (Meity) took the initiative to build a standard based uniform authentication framework/ service named "e-Pramaan".
e-Pramaan Authentication Levels
e-Pramaan is a standards-based National e-Authentication framework, which facilitates the authentication and security of users accessing various services on mobile and fixed platforms. It is a unique mechanism providing a unified log-in facility through SAML 2.0 based Single Sign-On (SSO) for integrated services. The Single Sign-On feature provides registered users with single window access to all services that are integrated with e-Pramaan.
It offers multi-factor authentication using (password, OTP, digital certificate and biometrics), with additional features comprising configurable chaining of authentication factors, web-site authentication, Aadhaar-based user identity verification and Driving License-based identity verification. This identity-based verification helps to map a virtual identity to a real one.
e-Pramaan is designed to work in tandem with projects like Aadhaar. It aims to consolidate disparate identity documents across government departments including driving license, PAN Etc. under a single digital profile.
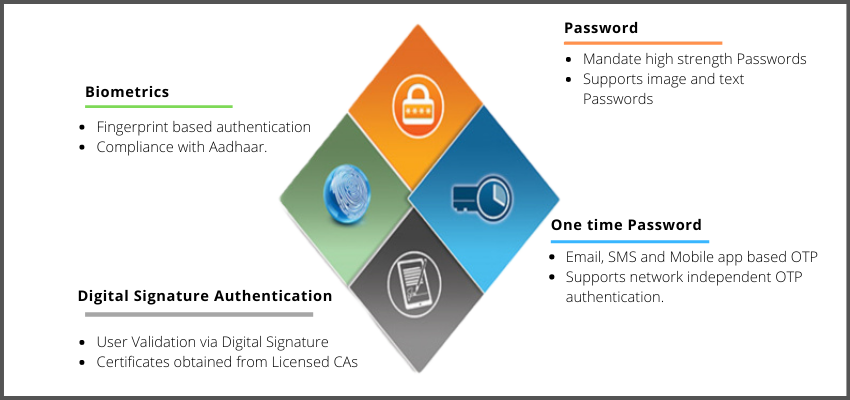
- Text Password: It is the most commonly used authentication. In e-Pramaan, the password data is stored in a secured manner to maintain confidentiality and hence can’t be retrieved.
- Image Password: Image Password was introduced in e-Pramaan as a language-neutral option that is also independent of the competencies of the individuals.
- strong>One Time Password (OTP): OTP helps in overcoming the replay attacks. e-Pramaan can send OTP on the user’s registered and verified mobile or email ID. e-Pramaan also gives a mobile app which can generate an OTP on the user’s registered and verified smartphone. The app is available on https://apps.mgov.gov.in/descp.do?appid=1120
- Digital Signature Certificate (DSC): e-Pramaan accepts the DSC of an authorized Indian CA as a secondary form of authentication. This, although more expensive than other options, it is more secure.
- Biometric: Biometric authentication is supported if the user has validated Aadhaar Number. Currently, fingerprint and IRIS based authentications are supported by e-Pramaan through Aadhaar.
e-Pramaan levels of authentication
Benefits for Integrated Services
Other than the benefits such as cost, time and effort effectiveness, the services integrated with e-Pramaan receive below mentioned benefits.
- Security - Information shared by e-Pramaan with services is encrypted using a symmetric key which is unique for every integrated service of e-Pramaan. In addition, e-Pramaan uses SSL to secure the communication channel between the user and e-Pramaan.
- Easy upgrade of authentication schemes: A service gets the flexibility of choosing authentication chaining. In authentication chaining, a service can choose various combinations of authentication types.
- Multi-technology support: Adapters for e-Pramaan integration is available for varied technologies like Java, .Net, PHP, etc.
- First Level Authorization: Services have the provision to map users to roles using the service portal.

e-Pramaan Integrated Services
Benefits for Users
As discussed before, the user gets a single window to access multiple services and hence doesn't have to remember a large number of logins and passwords. The user also gets the assurance that the website (s)he is accessing is not a phishing one and the user data is secured at rest and in transit.
e-Pramaan is also available as a mobile app on https://apps.mgov.gov.in/descp.do?param=0&appid=1265&fb=true
As discussed before, e-Pramaan provides biometrics-based authentication using Aadhaar services. e-Pramaan also uses Aadhaar services to map a user's virtual identity to the real one. A complete Aadhaar ecosystem is built which also provides Aadhaar based services independently.
Aadhaar based Authentication and e-KYC Services (ASA-AUA)
C-DAC is empanelled with UIDAI as an Authentication Service Agency (ASA), e-KYC Service Agency (KSA) and Authentication User Agency (AUA) for providing Aadhaar based authentication and e-KYC Services. C-DAC is connected with UIDAI’s Central Identities Data Repository (CIDR) through dedicated network lines for providing secure and prompt authentication service. C-DAC’s ASA and AUA services are available to government departments as well as to registered private organizations.
Services provided by C-DAC ASA AUA are
- Authentication Service: Provides instant verification and identification of the resident against the available data in CIDR. This includes demographic, biometric and OTP based authentication.
- One Time Password (OTP) Service: An OTP is sent to the registered mobile.
- e-KYC Service: UIDAI provide demographic and photographic information of the Aadhaar holder to the desired service provided that the user has given his/her consent.
- Best Finger Detection (BFD) Service: To identify the best finger for improved authentication accuracy.
Thus the authentication services provided by e-Pramaan will go a long way in realising the dream of Digital India, in true sense.
By
Dr Padmaja Joshi
Senior Director
C-DAC, Mumbai
- Blog
- National Common Mobility Card - A Single Card for a Gamut of Digital Transactions
- Emergency Response Support System: A big step in reaching out to the distressed
- e-Pramaan: A National Authentication Service along with Aadhaar
- m-Consultation through e-Sushrut Integrated Mobile App
- Central Dashboard: Performance Indicator of Drugs Supply Chain at National level in MoHFW, GoI
- e-RaktKosh (Centralized Blood Bank Management System)